LoRa backscatter communications: Temporal, spectral, and error performance analysis
About
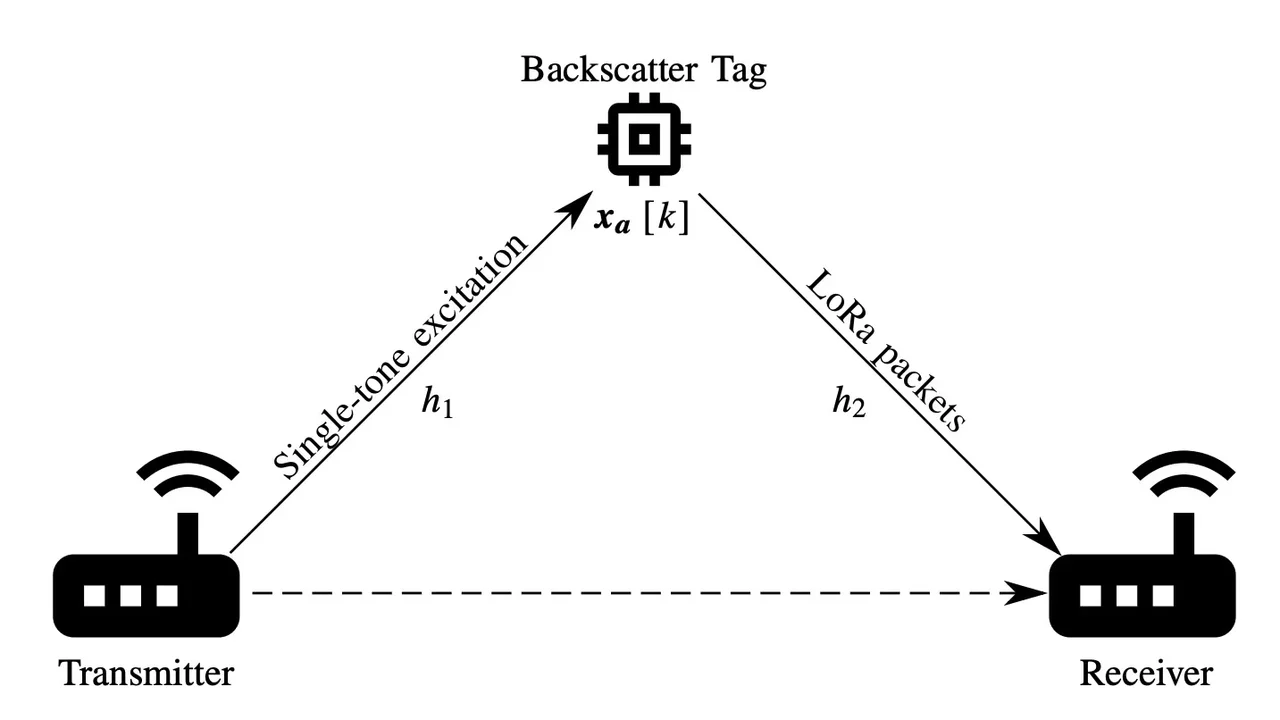
LoRa backscatter (LB) communication systems can be considered as a potential candidate for ultra low power wide area networks (LPWAN) because of their low cost and low power consumption. In this paper, we comprehensively analyze LB modulation from various aspects, i.e., temporal, spectral, and error performance characteristics. First, we propose a signal model for LB signals that accounts for the limited number of loads in the tag. Then, we investigate the spectral properties of LB signals, obtaining a closed-form expression for the power spectrum. Finally, we derived the symbol error rate (SER) of LB with two decoders, i.e., the maximum likelihood (ML) and fast Fourier transform (FFT) decoders, in both additive white Gaussian noise (AWGN) and double Nakagami-m fading channels. The spectral analysis shows that out-of-band emissions for LB satisfy the European Telecommunications Standards Institute (ETSI) regulation only when considering a relatively large number of loads. For the error performance, unlike conventional LoRa, the FFT decoder is not optimal. Nevertheless, the ML decoder can achieve a performance similar to conventional LoRa with a moderate number of loads.
More information can be found in the video given below and the paper:
G. Lin, A. Elzanaty and M. -S. Alouini, "LoRa Backscatter Communications: Temporal, Spectral, and Error Performance Analysis," in IEEE Internet of Things Journal, doi: 10.1109/JIOT.2023.3268113.


